
|Why must static electricity be removed?
Because when static electricity is present, the following problems will occur.

These problems are caused by the following phenomena.

|Specifically, what problems may occur?
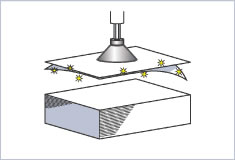
Absorption of multiple sheets
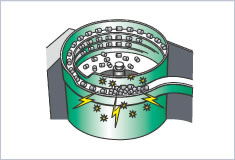
Clogging of parts feeders
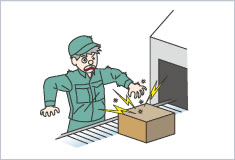
Discomfort due to electrical shocks in the workplace
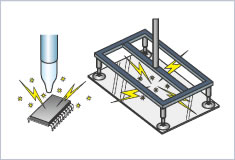
Electrostatic breakdown of substrate and IC chips
Failure to eject workpieces from unloaders
Uneven painting
|What is static electricity?

Electrons move simply as a result of physical contact between two objects. Electrons have negative polarity, so an object on which there are many electrons acquires a negative charge. Conversely, an object from which electrons have been stolen acquires a positive charge. Here, a description is given of the types of static electricity generation and also the triboelectric series.
Types of Static Electricity Generation
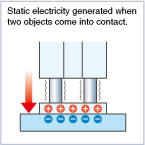
Contact Charging
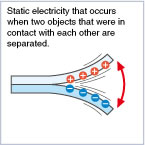
Separation Charging
Frictional Charging
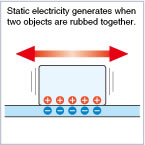
Clash Charging
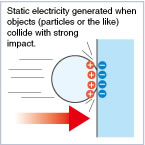
Vapor Charging
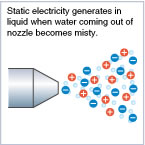
Rolling ChargingNoteNote)
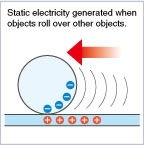
Induction Charging
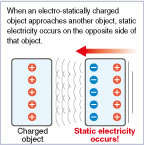
Charging from External Ion
Lightning is also static electricity.

Note:
The charging electric potential is greatly influenced by the energy applied to an object.
For example, in the case of rolling charging, the faster the charging speed, the higher becomes the charging electric potential.
Triboelectric series
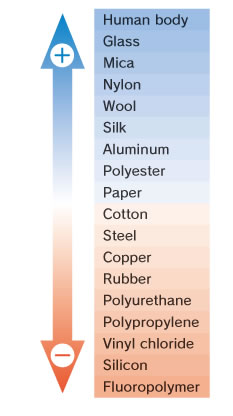
How to read the triboelectric series
The materials mentioned in the upper part of the triboelectric series are charged positively and those mentioned in the lower part are charged negatively.
Example 1: Glass (+) Polyester (‒)
Example 2: Polyester (+) Fluororesin (‒)
As the distance between 2 materials becomes greater, the amount of charge becomes larger.
Example 1: Amount of charge between the human body and nylon (Small)
Example 2: Amount of charge between the human body and polyurethane (Large)
It can be seen that some objects easily acquire a positive charge, while others easily acquire a negative charge, depending
upon the material of the object. Also, if objects consisting of materials located at greatly differing parts of the
table shown at left touch each other, the amount of static electricity will become large.
For example, if static electricity is generated by copper and rubber for the reason indicated in the figure at left, the copper
will acquire a positive charge, and the rubber will acquire a negative charge.
The charging electric potential acquired by the human body and fluororesin is larger than that acquired by copper and rubber.


